Example: (n,k) Block Code
This example is based on Proakis (2007, Example 7.2-1)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sympy import symbols, expand
from collections import Counter# Generator matrix G
G = np.array([
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]
])
# Compute the parity check matrix H
# Extract P from G (everything after the identity matrix)
P = G[:, 4:]
# H = [-P^T | I], but since in binary {-1 = 1},
# simply use P^T directly
k = G.shape[0] # k: message length
n = G.shape[1] # n: codeword length
n_minus_k = n - k # n_minus_k: parity bits
I_n_k = np.identity(n_minus_k, dtype=int)
H = np.concatenate((P.T, I_n_k), axis=1)
print("Generator matrix G:")
print(G)
print("\nParity-check matrix H:")
print(H)
Generator matrix G:
[[1 0 0 0 1 0 1]
[0 1 0 0 1 1 1]
[0 0 1 0 1 1 0]
[0 0 0 1 0 1 1]]
Parity-check matrix H:
[[1 1 1 0 1 0 0]
[0 1 1 1 0 1 0]
[1 1 0 1 0 0 1]]
Message, Codeword, Weight¶
# Function to compute the weight of a codeword
def weight(codeword):
return np.sum(codeword != 0)
# Generate all possible messages of length k
num_messages = 2**k
messages = np.array([[(i >> j) & 1 for j in range(k)][::-1] \
for i in range(num_messages)])
# Generate codewords and compute their weights
codewords = np.dot(messages, G) % 2
weights = np.array([weight(codeword) for codeword in codewords])
# Collecting messages, codewords, and their weights in a structured format
message_codeword_weight = [{"Message": m.tolist(), \
"Codeword": cw.tolist(), \
"Weight": w} for m, cw, w in \
zip(messages, codewords, weights)]
# Output the structured data
message_codeword_weight
[{'Message': [0, 0, 0, 0], 'Codeword': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], 'Weight': 0},
{'Message': [0, 0, 0, 1], 'Codeword': [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1], 'Weight': 3},
{'Message': [0, 0, 1, 0], 'Codeword': [0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0], 'Weight': 3},
{'Message': [0, 0, 1, 1], 'Codeword': [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1], 'Weight': 4},
{'Message': [0, 1, 0, 0], 'Codeword': [0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1], 'Weight': 4},
{'Message': [0, 1, 0, 1], 'Codeword': [0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0], 'Weight': 3},
{'Message': [0, 1, 1, 0], 'Codeword': [0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], 'Weight': 3},
{'Message': [0, 1, 1, 1], 'Codeword': [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0], 'Weight': 4},
{'Message': [1, 0, 0, 0], 'Codeword': [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1], 'Weight': 3},
{'Message': [1, 0, 0, 1], 'Codeword': [1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0], 'Weight': 4},
{'Message': [1, 0, 1, 0], 'Codeword': [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1], 'Weight': 4},
{'Message': [1, 0, 1, 1], 'Codeword': [1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0], 'Weight': 3},
{'Message': [1, 1, 0, 0], 'Codeword': [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], 'Weight': 3},
{'Message': [1, 1, 0, 1], 'Codeword': [1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1], 'Weight': 4},
{'Message': [1, 1, 1, 0], 'Codeword': [1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0], 'Weight': 4},
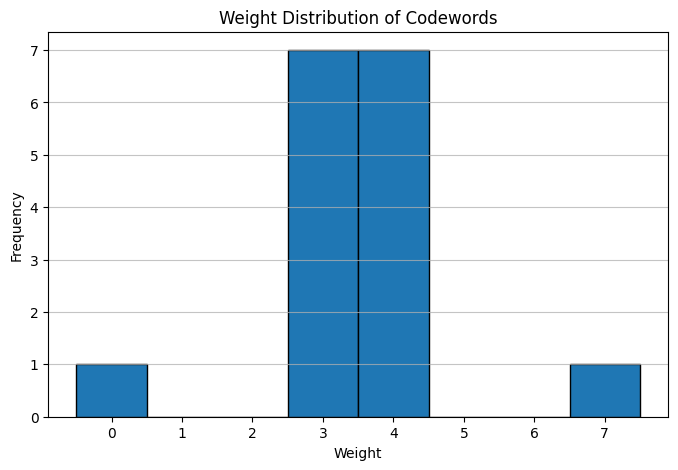
{'Message': [1, 1, 1, 1], 'Codeword': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], 'Weight': 7}]Weight Distribution¶
# Plot the weight distribution as a histogram
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.hist(weights, \
bins=np.arange(weights.min(), weights.max() + 2) \
- 0.5, ec='black')
plt.title('Weight Distribution of Codewords')
plt.xlabel('Weight')
plt.ylabel('Frequency')
plt.xticks(range(min(weights), max(weights) + 1))
plt.grid(axis='y', alpha=0.75)
plt.show()
Two conditions:¶
- for a valid codeword , to ensure it meets the code’s parity check.
- , to verify the correctness of our generator and parity check matrices.
# Check condition cH^T = 0 for the example codeword
c_H_transpose = np.dot(codewords, H.T) % 2
# Check condition GH^T = 0
G_H_transpose = np.dot(G, H.T) % 2
(c_H_transpose, G_H_transpose)
(array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]]),
array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]]))Hamming distance¶
# Initialize matrices to store the Hamming distances
# and the weight of differences
hamming_distances = np.zeros((num_messages, num_messages), dtype=int)
weight_difference = np.zeros((num_messages, num_messages), dtype=int)
# Iterate through all pairs of codewords
for i in range(num_messages):
for j in range(num_messages):
# Compute the difference between codewords
# this is also a codeword
difference = codewords[i] - codewords[j]
# Compute the Hamming distance as the weight
# of the bitwise difference
hamming_distance = np.sum(difference != 0)
# Store the computed Hamming distance
hamming_distances[i, j] = hamming_distance
# Store the weight of the bitwise difference
weight_difference[i, j] = weight(difference)
print("Hamming Distances:\n", hamming_distances)
print("Weight of Difference:\n", weight_difference)
Hamming Distances:
[[0 3 3 4 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 3 4 4 7]
[3 0 4 3 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 4 3 7 4]
[3 4 0 3 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 4 7 3 4]
[4 3 3 0 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 7 4 4 3]
[4 3 3 4 0 3 3 4 3 4 4 7 3 4 4 3]
[3 4 4 3 3 0 4 3 4 3 7 4 4 3 3 4]
[3 4 4 3 3 4 0 3 4 7 3 4 4 3 3 4]
[4 3 3 4 4 3 3 0 7 4 4 3 3 4 4 3]
[3 4 4 3 3 4 4 7 0 3 3 4 4 3 3 4]
[4 3 3 4 4 3 7 4 3 0 4 3 3 4 4 3]
[4 3 3 4 4 7 3 4 3 4 0 3 3 4 4 3]
[3 4 4 3 7 4 4 3 4 3 3 0 4 3 3 4]
[3 4 4 7 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 0 3 3 4]
[4 3 7 4 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 3 0 4 3]
[4 7 3 4 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 3 4 0 3]
[7 4 4 3 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 4 3 3 0]]
Weight of Difference:
[[0 3 3 4 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 3 4 4 7]
[3 0 4 3 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 4 3 7 4]
[3 4 0 3 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 4 7 3 4]
[4 3 3 0 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 7 4 4 3]
[4 3 3 4 0 3 3 4 3 4 4 7 3 4 4 3]
[3 4 4 3 3 0 4 3 4 3 7 4 4 3 3 4]
[3 4 4 3 3 4 0 3 4 7 3 4 4 3 3 4]
[4 3 3 4 4 3 3 0 7 4 4 3 3 4 4 3]
[3 4 4 3 3 4 4 7 0 3 3 4 4 3 3 4]
[4 3 3 4 4 3 7 4 3 0 4 3 3 4 4 3]
[4 3 3 4 4 7 3 4 3 4 0 3 3 4 4 3]
[3 4 4 3 7 4 4 3 4 3 3 0 4 3 3 4]
[3 4 4 7 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 0 3 3 4]
[4 3 7 4 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 3 0 4 3]
[4 7 3 4 4 3 3 4 3 4 4 3 3 4 0 3]
[7 4 4 3 3 4 4 3 4 3 3 4 4 3 3 0]]
hamming_distances - weight_differencearray([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])Minimum Distance¶
num_messages = len(codewords) # Number of codewords/messages
# Remove the diagonal elements for the search of
# the minimum non-zero Hamming distance
np.fill_diagonal(hamming_distances, np.max(hamming_distances) + 1)
# Finding d_min from the adjusted Hamming distances
d_min = np.min(hamming_distances)
print("Minimum Hamming Distance (d_min):", d_min)
Minimum Hamming Distance (d_min): 3
Minimum Weight¶
# Can use the above method for d_min or use the following:
# Finding the minimum weight using the codewords directly
# The minimum weight of a code is the minimum
# of the weights of all nonzero codewords
# Initialize the minimum weight to a large value
# before finding the actual minimum
min_weight_codewords = np.inf
# Iterate through all codewords to find the minimum non-zero weight
for codeword in codewords:
cw_weight = weight(codeword)
if 0 < cw_weight < min_weight_codewords:
min_weight_codewords = cw_weight
min_weight_codewords
print("Minimum Weight (w_min):", min_weight_codewords)
Minimum Weight (w_min): 3
WEP, Eq. 7.2-30¶
# Count the occurrence of each weight
weight_counts = Counter(weights)
# The maximum weight is the length of a codeword
max_weight = len(codewords[0])
# Initialize a list for coefficients with zeros
wep_coefficients = [0] * (max_weight + 1)
# Populate the coefficients based on weight counts
for weight, count in weight_counts.items():
wep_coefficients[weight] = count
# Construct the WEP as a string for display
# Eq. 7.2-30
wep_str = " + ".join(f"{coef} Z^{i}" for i, coef \
in enumerate(wep_coefficients) if coef > 0)
wep_str
'1 Z^0 + 7 Z^3 + 7 Z^4 + 1 Z^7'IOWEF, ¶
# Calculate the weight of each codeword
codeword_weights = np.sum(codewords, axis=1)
# Calculate the weight of each information sequence (message)
message_weights = np.sum(messages, axis=1)
# Function to count B_ij
def count_B_ij(codeword_weights, message_weights, i, j):
return np.sum((codeword_weights == i) & (message_weights == j))
# Count B_31, B_42, B_74
B_31 = count_B_ij(codeword_weights, message_weights, 3, 1)
B_42 = count_B_ij(codeword_weights, message_weights, 4, 2)
B_74 = count_B_ij(codeword_weights, message_weights, 7, 4)
B_31, B_42, B_74
(3, 3, 1)# Function to find information sequences and
# corresponding codewords for given B_ij values
def find_sequences_codewords(codewords, messages, \
codeword_weights, message_weights, i, j):
indices = np.where((codeword_weights == i) & (message_weights == j))[0]
return [(messages[index], codewords[index]) for index in indices]
# Find sequences and codewords for B_31, B_42, B_74
sequences_codewords_B_31 = \
find_sequences_codewords(codewords, messages, \
codeword_weights, message_weights, 3, 1)
sequences_codewords_B_42 = \
find_sequences_codewords(codewords, messages, \
codeword_weights, message_weights, 4, 2)
sequences_codewords_B_74 = \
find_sequences_codewords(codewords, messages, \
codeword_weights, message_weights, 7, 4)
sequences_codewords_B_31, sequences_codewords_B_42, \
sequences_codewords_B_74
([(array([0, 0, 0, 1]), array([0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1])),
(array([0, 0, 1, 0]), array([0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0])),
(array([1, 0, 0, 0]), array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]))],
[(array([0, 0, 1, 1]), array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1])),
(array([1, 0, 0, 1]), array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0])),
(array([1, 0, 1, 0]), array([1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1]))],
[(array([1, 1, 1, 1]), array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]))])(from Example 7.2-2)
For ¶
- Information Sequence: , Codeword:
- Information Sequence: , Codeword:
- Information Sequence: , Codeword:
For ¶
- Information Sequence: , Codeword:
- Information Sequence: , Codeword:
- Information Sequence: , Codeword:
For ¶
- Information Sequence: , Codeword:
# Define the symbol Z
Z = symbols('Z')
# Calculate the weight distribution polynomial A(Z)
# for (7,4) Hamming code
# Eq. 7.3-2
A_Z_eq_7_3_2 = (1 / (n + 1)) * ((1 + Z)**n \
+ n*(1 + Z)**int((n - 1) / 2) \
* (1 - Z)**int((n + 1) / 2))
# Expand the polynomial for clarity
A_Z_expanded_final = expand(A_Z_eq_7_3_2)
A_Z_expanded_final # same result as Eq. 7.2-30
Loading...
Error vector/pattern ¶
# n is defined previously as the length of the codewords
# To generate all possible 2^n error patterns including
# the zero vector for an (n, k) code
error_patterns = [np.array(list(np.binary_repr(i, width=n)), dtype=int) \
for i in range(2**n)]
print("Error patterns:")
error_patterns
Error patterns:
[array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]),
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])]Syndrome¶
# Calculate the syndrome for each error pattern
syndromes = np.dot(error_patterns, H.T) % 2
# Present all unique syndromes
unique_syndromes = np.unique(syndromes, axis=0)
# Output
syndromes, unique_syndromes
(array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0]]),
array([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1]]))# Count how many syndromes are there
total_syndromes = syndromes.shape[0]
# Count how many unique syndromes are there
total_unique_syndromes = unique_syndromes.shape[0]
total_syndromes, total_unique_syndromes(128, 8)- Proakis, J. (2007). Digital Communications (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional.